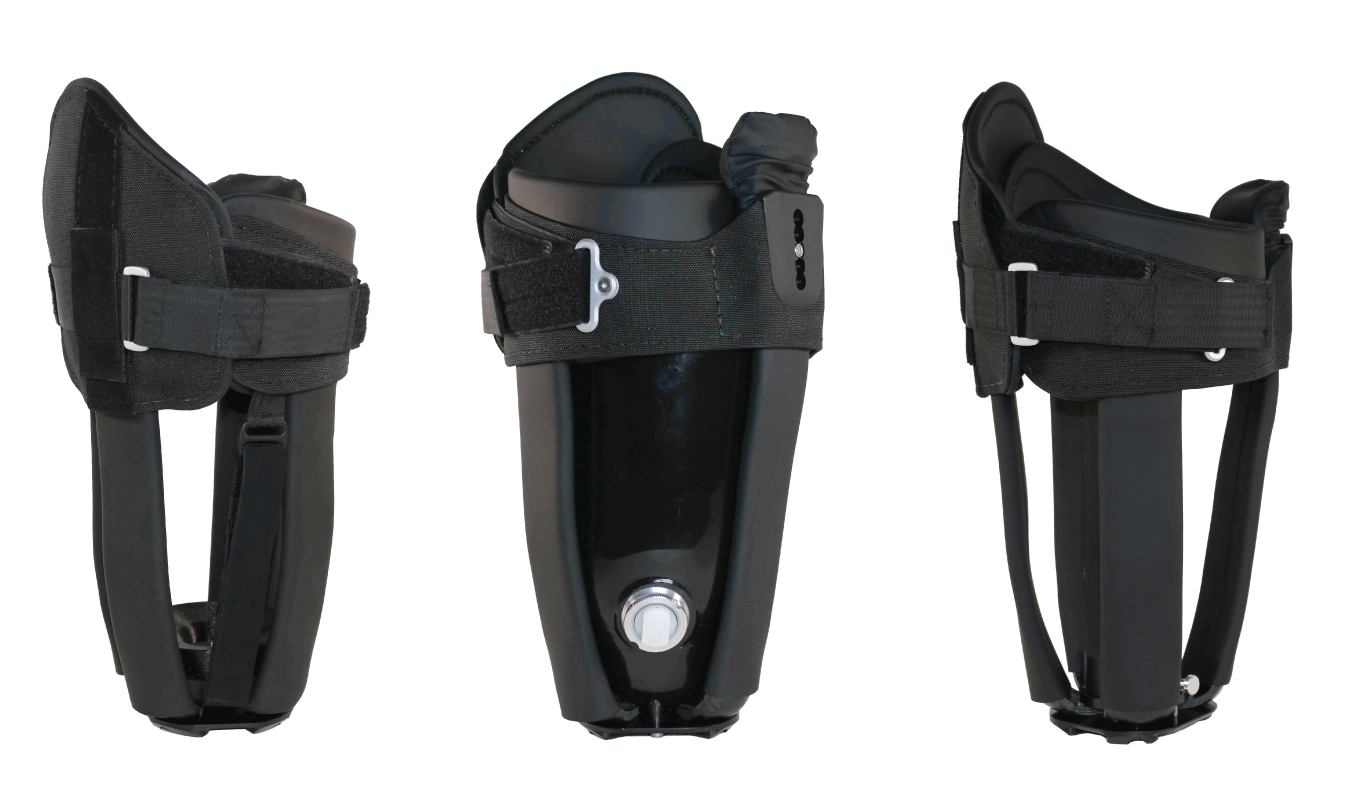
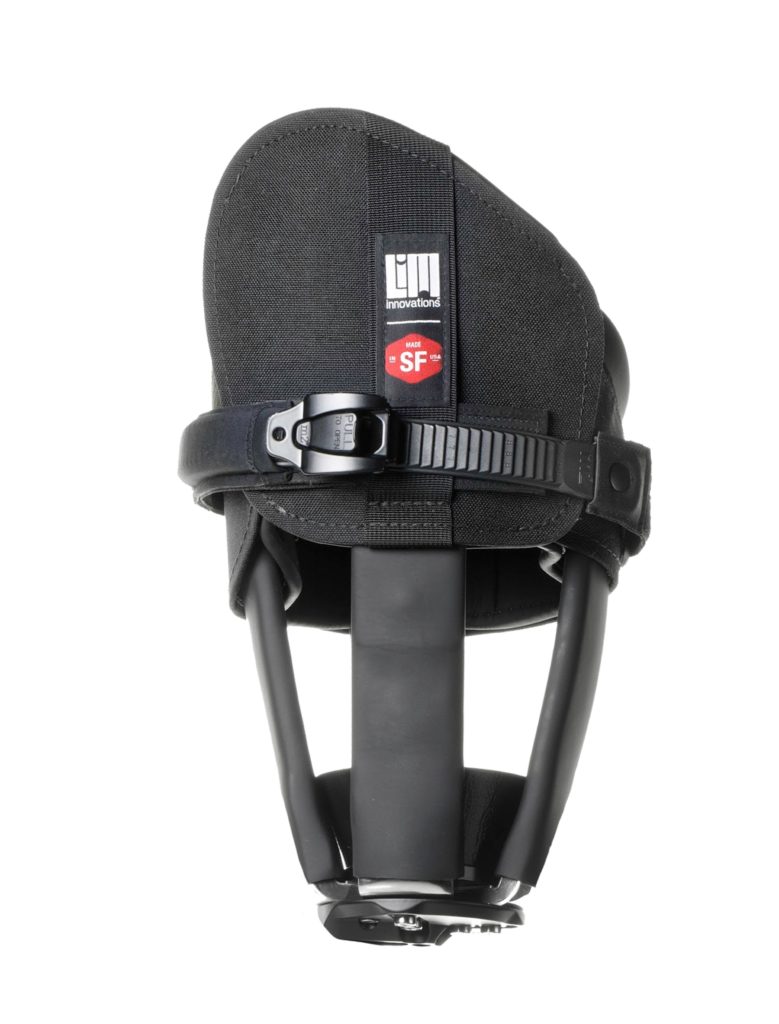
The most comfortable and adjustable custom socket for above-knee amputees. Every aspect of the Infinite Socket™ TF was designed and engineered with comfort and lifestyle in mind. The Infinite Socket™ TF mimics human anatomy to provide improved function, adjustability, and comfort.

Precise Adjustability
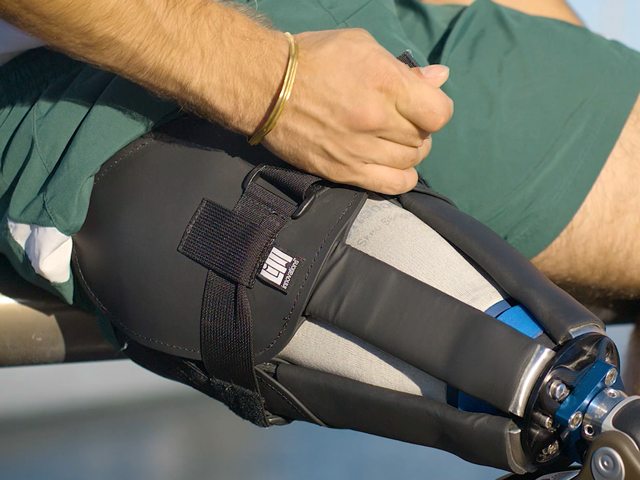

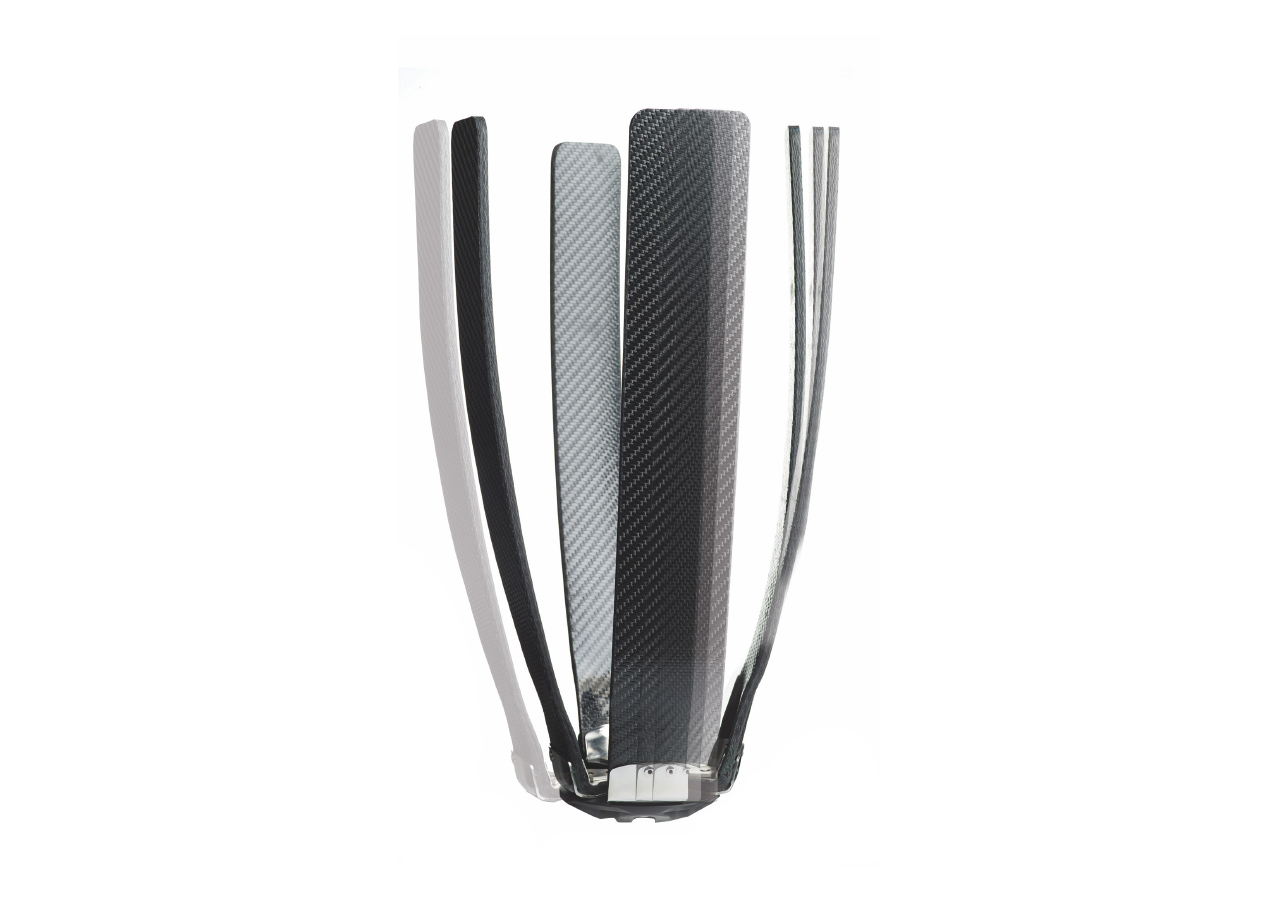
The Infinite Socket™ TF adjustable components enable both patients and clinicians to fine-tune fit for better comfort and control. A modular frame and carbon fiber struts make it easy for prosthetists to make modifications in response to body fluctuations. The built-in, anti-microbial, flexible brim can be loosened when sitting and tightened when walking to achieve optimal stability and comfort.
Dynamic Frame
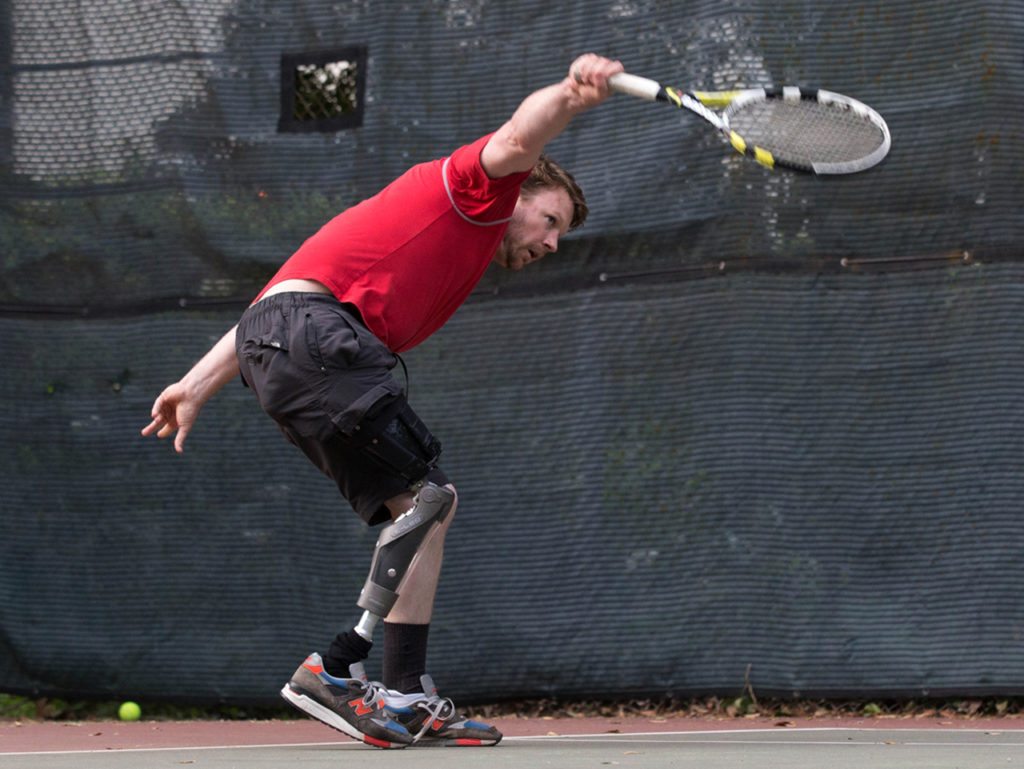

The structural frame is designed to flex or spring like a bike frame or ski boot.
Improved Pressure Distribution
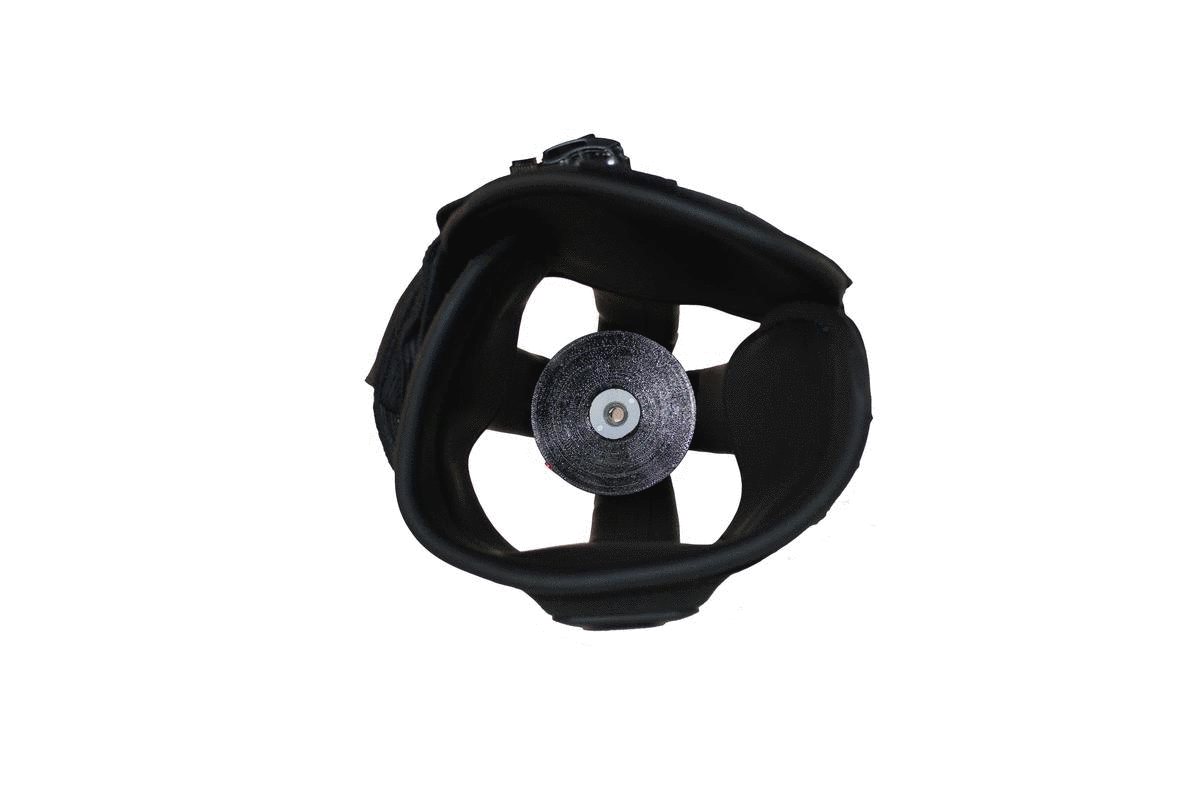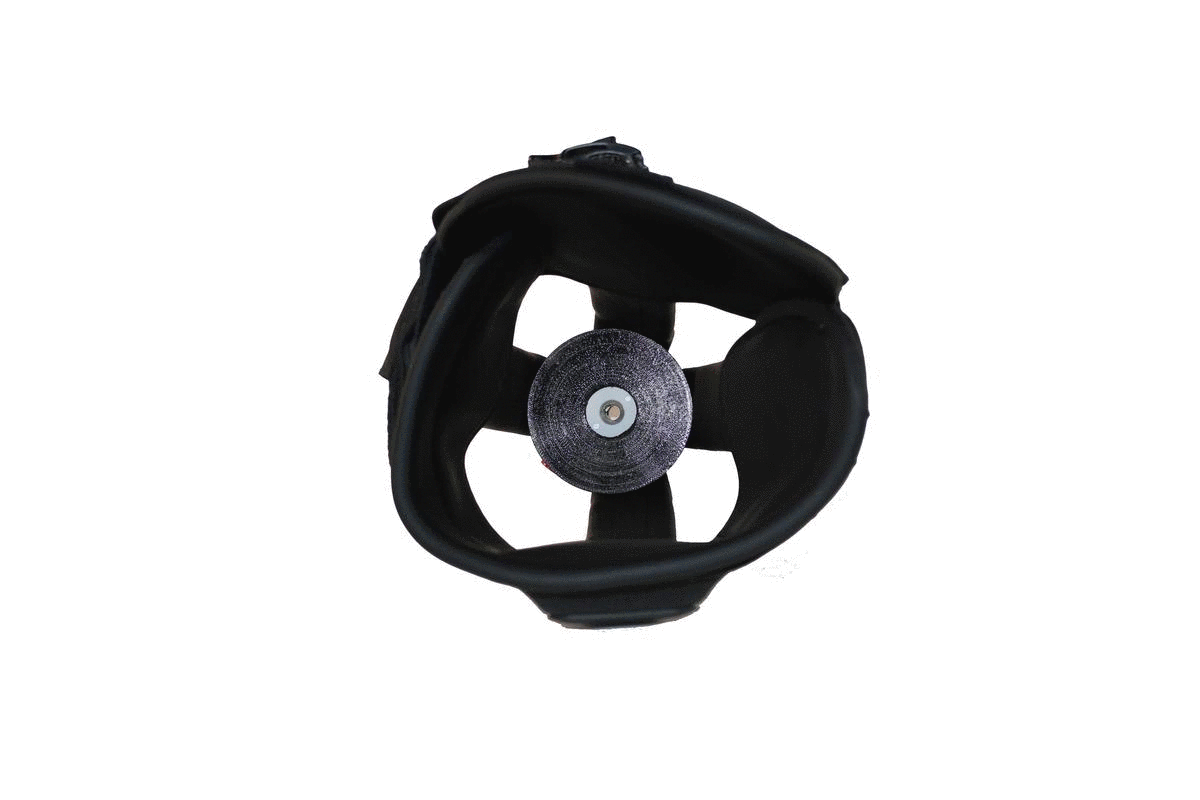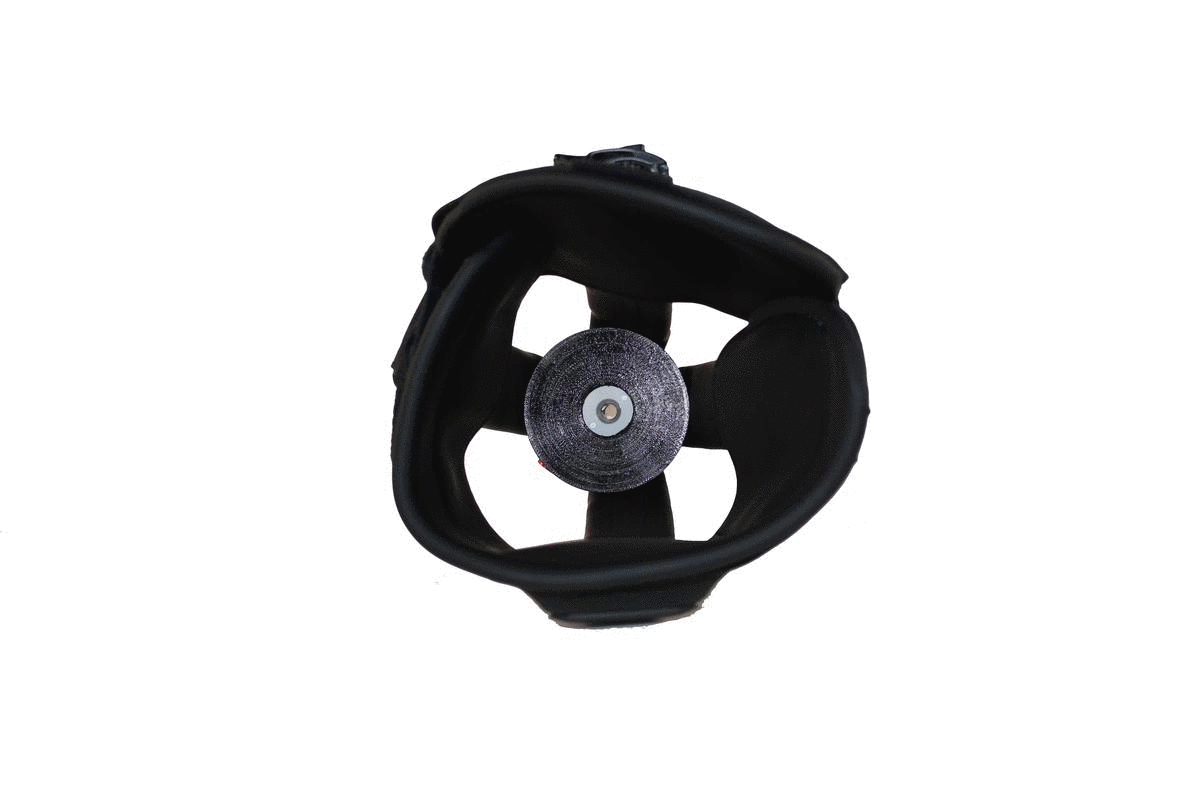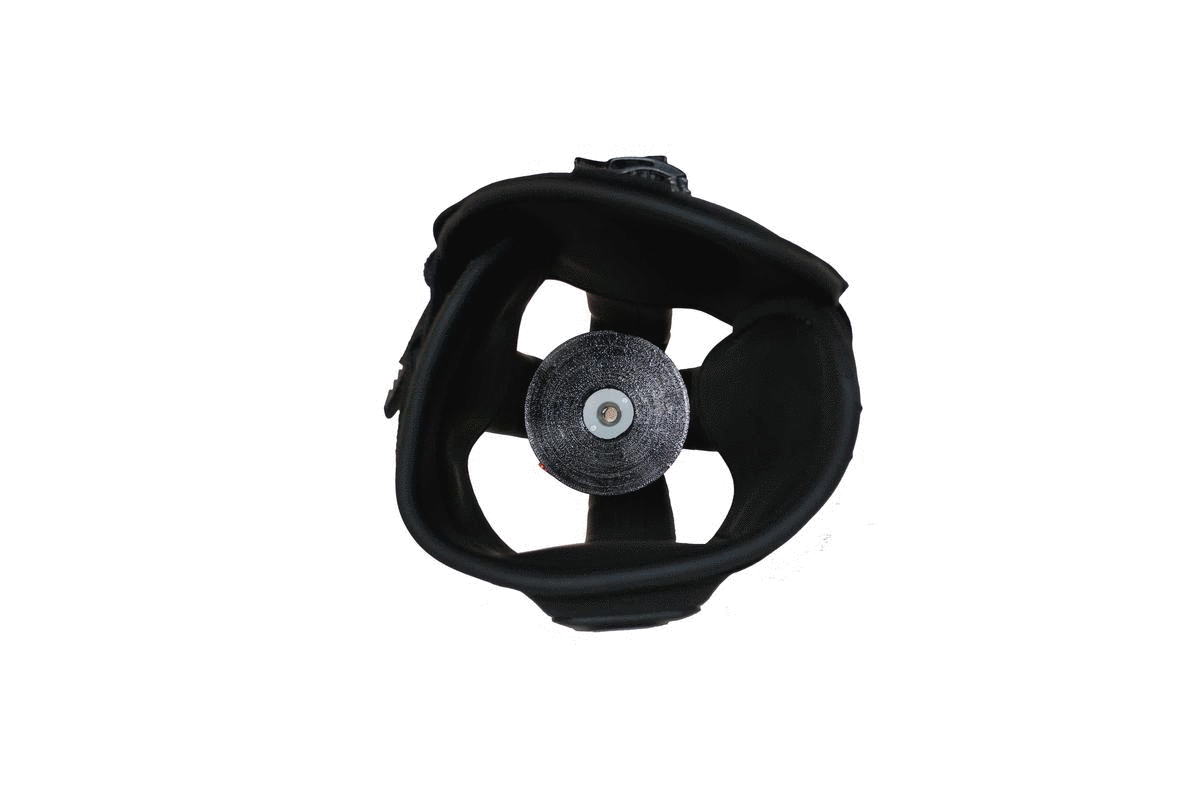
With integrated textiles and adjustable components, the Infinite Socket™ TF conforms seamlessly to the limb and enables superior comfort. Height adjustments on the ischial seat and medial brim on the Infinite Socket™ TF reduce weight-bearing on neuromas.
Reimbursement Information
In the United States, prosthetists must classify the components of a prosthesis according to standard billing codes, called L-codes. LIM Innovations, as well as other industry manufacturers, suggests L-codes for their products. It is the responsibility of prosthetists to use correct coding when submitting information to Medicare and private insurance companies.